Products >> Rigid-Flex Assembly
Rigid-Flex Assembly
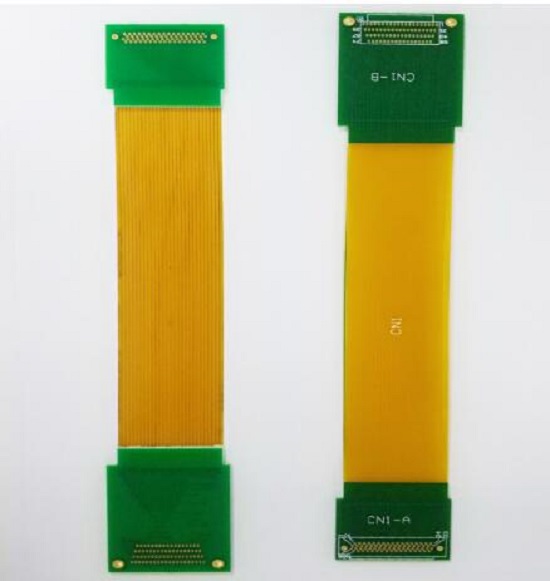
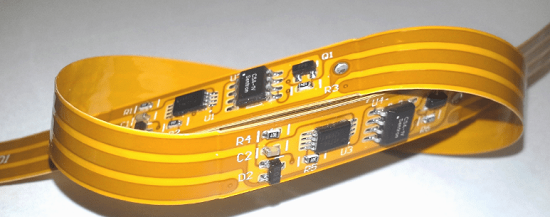
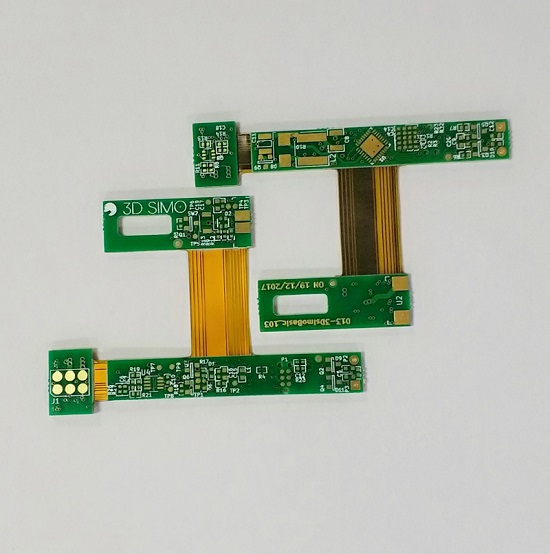
Unlike a conventional PCB stack-up, foil construction cannot be used for flex layers. The flex layers in a rigid-flex assembly are built from unreinforced base substrates typically consisting of polyimide dielectric film, clad with rolled annealed copper. The rolled copper is much more flexible than the copper used for rigid boards, but it cannot be plated without becoming brittle. Therefore, the clad base material is first drilled, holes are selectively plated, then the traces and pads are etched. Bondply, a layer of polyimide film with adhesive coating on both sides, isolates that conductor layer from the next, and so forth. A cover layer of adhesive polyimide film insulates and protects the top and bottom surfaces of the flex stack along the ribbon that extends between rigid PCB sections.
Flex materials are elastic under all circumstances, including processing. During the final lamination of the rigid-flex stack, they are less dimensionally stable than the rigid core and prepreg materials that sandwich them. Hole to copper clearance must be greater than the minimum possible with a rigid-only stack-up, ideally at least 10 mils. Vias must be farther from the edge of the rigid area adjoining the flex ribbon than the minimum distance in rigid-only stacks, preferably at least 50 mils from the edge, but certainly no less than 30 mils. This rule is the one most violated in rigid-flex designs.




Products Category
- PCB Design & Layout
- PCB manufacturing
- PCB Assembly
- BGA Assembly
- THT Assembly
- SMT Assembly
- Mixed PCB Assembly in Electronic PCBA
- Single sided PCB assembly
- Double sided PCB assembly
- Rigid-Flex Assembly
- COB Bonding Manufacturing
- Components sourcing for PCB Assembly
- SMT Stencils
- Box build assembly
- PCB engineer reverse
Contact Us
E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected]
Skype: [email protected]
Whatsapp: +86 15012972502
Add: 2F, BUILDING H, WANDA INDUSTRIAL ZONE, ZHOUSHI ROAD, LANGXIN COMMUNITY,SHIYAN STREET, BAO 'AN DISTRICT, SHENZHEN, GUANGDONG, CHINA
Link







 Skype Chat
Skype Chat WhatsApp
WhatsApp  Mail inquiry
Mail inquiry